1735 words
9 minutes
Game of Life 만들기
규칙
Game of Life은 간단한 2가지의 규칙으로 돌아간다.
- 죽은 칸에 접한 8칸 중 정확히 3칸에 세포가 살아 있다면 해당 칸의 세포는 그 다음 세대에 살아난다.
- 살아있는 칸과 접한 8칸 중 2칸미만 또는 3칸초과의 세포가 살아 있다면 해당 칸의 세포는 죽는다.
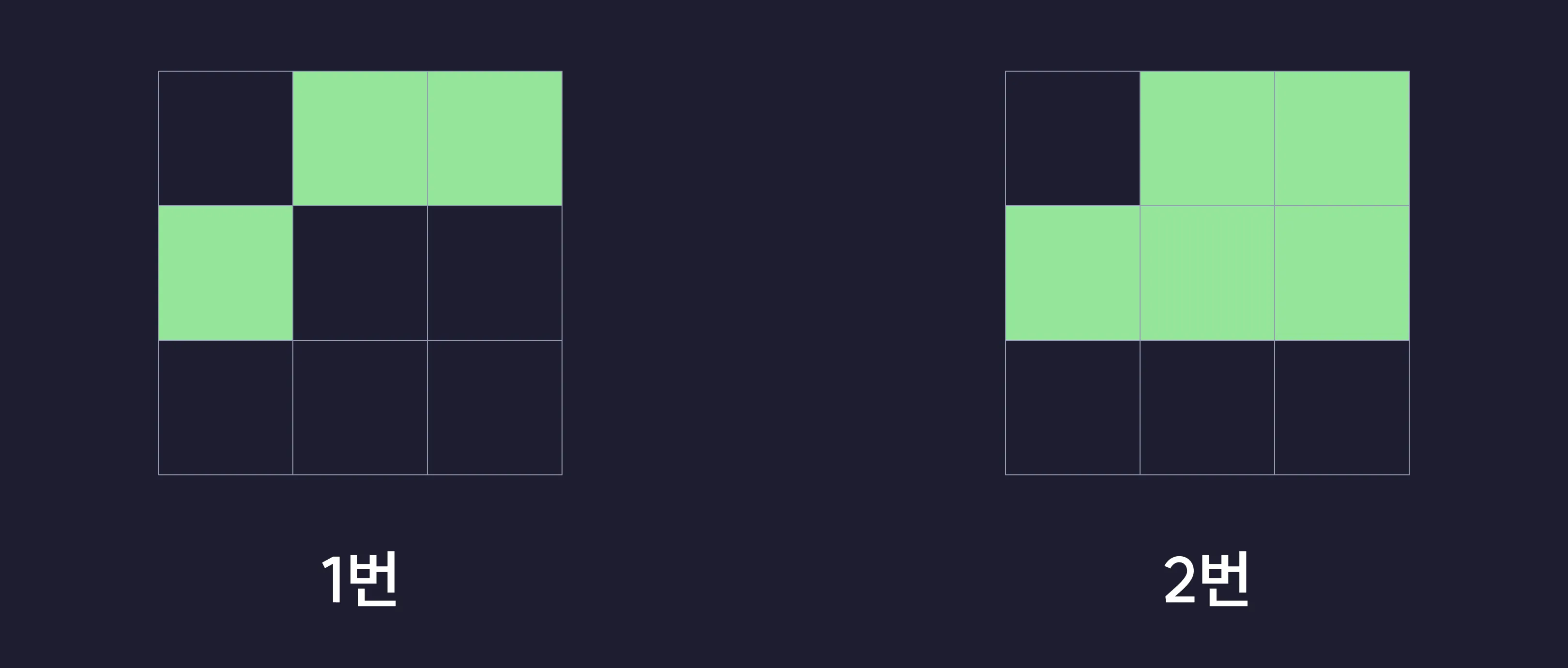
- 1번 사진은 중항을 기준으로 근처에 3칸의 살아있는 세포가 있으니 살아난다.
- 2번 사진은 중항을 기준으로 근처에 2칸 미만 또는 3칸 초과의 살아있는칸이 있으니 세포가 죽는다.
알고리즘 생각하기
- 죽어있는 세포와 살아있는 세포의 위치를 모두 배열에 넣는다.
- 살아있는 세포의 위치 인덱스만을 모아놓은 배열을 만들어 구현한다.
이런식으로 2가지방법이 있다.
- 1번 방법의 경우 구현하기는 2번보다 쉽지만 맵을 크게 만들기에는좀 무리가 있다.
- 2번 방법의 경우에는 구현하기가 좀 어렵지만 맵을 크게구현해도 세포의 살아있는칸의 위치만 기억하니 용량도 적고 최적화도 잘된다.(그리고 맵을 무한하게도 만들수 있다)
프로젝트 초기화하기
이제 프로젝트를 초기화해보자
명령어
cargo install wasm-pack
wasm-pack new game-of-life
cd life-of-game
src > lib.rs
mod utils;
use wasm_bindgen::prelude::*;
Cargo.toml
Cargo.toml은 이렇게바꿔준다
프로그래밍 시작
이제 Game of Life을 만들어보자
enum, struct만들기
enum을 통해서 세포의 상태를 만드는 이유는 세포의 상태를 직관적으로 상태를 볼 수 있기 때문에 사용한다
#[wasm_bindgen] // wasm으로 빌드하기위해 wasm_bindgen매크로를 써준다.
#[derive(Clone, Copy, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)] // 나중에 비교, 복사, 출력 등을 할수있으니 추가해준다
pub enum Cell {
Dead,
Alive,
}
#[wasm_bindgen]
pub struct LifeOfGame {
alives: Vec<(isize, isize)>, // 살아있는 세포의 위치
camera: (isize, isize), // 카메라의 위치(렌더링할떄 일정 부분만 보이게 하기위해 넣는다)
}
#[wasm_bindgen]
impl LifeOfGame {
// 그냥 평범한 초기화 코드
pub fn new() -> Self {
Self {
alives: vec![],
camera: (0, 0),
}
}
}
세포 삽입/삭제 구현
alives배열을 쉽게 관리하기위해 set메서드를 만든다.
#[wasm_bindgen]
impl LifeOfGame {
// ..생략
fn set(&mut self, i: isize, j: isize, state: Cell) {
if state == Cell::Dead {
// (i, j)에 살아있는 세포가 없으면 이미 죽어있는거니 굳이 안죽인다
if self.alives.contains(&(i, j)) {
self.alives.remove(
// (i, j)에 위치한 살아있는 세포의 인덱스를 가저옴
self.alives
.iter()
.enumerate()
.find(|x| x.1 == &(i, j))
.unwrap()
.0,
);
}
} else {
// (i, j)에 살아있는 세포가 있음면 이미 살아있는거니 추가하지 않는다
if !self.alives.contains(&(i, j)) {
self.alives.push((i, j));
}
}
}
}
세포 값 변경하기
아까만든 set메서드를 활용해서 값을 반전시키는 메서드를 만든다.
#[wasm_bindgen]
impl LifeOfGame {
// ..생략
pub fn toggle(&mut self, i: isize, j: isize) {
if self.alives.contains(&(i, j)) {
self.set(i, j, Cell::Dead)
} else {
self.set(i, j, Cell::Alive)
}
}
}
다음값 확인하기
#규칙에 있는걸 확인하여 1번 실행하는 step메서드를 만들어준다.
#[wasm_bindgen]
impl LifeOfGame {
// ..생략
pub fn step(&mut self) {
// 한번에 바꾸지 않고 조금씩 바꾸면 문제가 생길수있으니 백터를 만들어 해결행다
let mut changes = vec![];
// 규칙에서 살아있는 세포의 위치만 확인하니 반복문에 넣어서 돌린다.
for alive in &self.alives {
let mut count = 0;
// 살아있는 세포에 이웃한 인덱스를 받아오기위해 -1부터 1까지 반복문에 넣는다
for i in -1..=1 {
for j in -1..=1 {
// 자신을 제외하고 카운트한다
if i == 0 && j == 0 {
continue;
}
let x = alive.0 as i32 + i;
let y = alive.1 as i32 + j;
{
let mut count = 0; // 변수를 가릴수 있는걸 이용하여 변수를 만들어준다
// 위 반복문가 같은이유로 이런식으로 돌린다
for k in -1..=1 {
for l in -1..=1 {
let xx = x + k;
let yy = y + l;
count += self.alives.contains(&(xx as isize, yy as isize)) as i32;
}
}
// 살아있는세포가 3개면 새로운 세포가 태어난다
if count == 3 {
changes.push((x as isize, y as isize, Cell::Alive));
}
}
count += self.alives.contains(&(x as isize, y as isize)) as i32;
}
}
// 살아있는세포가 2보다 작거나 3보다 크면 죽는다
if 2 > count || count > 3 {
changes.push((alive.0, alive.1, Cell::Dead));
}
}
// 위에서 변경한다고 해준값을 반복문을통해 변경해준다
for data in &changes {
self.set(data.0, data.1, data.2)
}
}
}
그리기
#[wasm_bindgen]
impl LifeOfGame {
// 자신이 보고있는부분을움직아는 메서드
pub fn move_camera(&mut self, x: isize, y: isize) {
self.camera.0 += x;
self.camera.1 += y;
}
pub fn draw(&self, width: isize, height: isize) {
let doc = web_sys::window().unwrap().document().unwrap(); // js의 document와 같은 객채를 가저옴
let game = doc.get_element_by_id("game").unwrap(); // game이라는 id를 가진값을 가저옴
let mut html = String::new();
// id가 {i},{j}인 타일들을 그림
for i in self.camera.1..(height + self.camera.1) {
html.push_str("<div>");
for j in self.camera.0..(width + self.camera.0) {
html.push_str(&format!(
"<div type='button' id='{i},{j}' class='tile' {}></div>",
if self.alives.contains(&(i as isize, j as isize)) {
"alive" // 살아있을경우 alive attr을 추가해서 놔둠
} else {
""
}
));
}
html.push_str("</div>");
}
game.set_inner_html(&html);
}
}
빌드하기
이제 wasm의 코드를 다 만들었으니 이 코드를 빌드해보자
아레 코드를쓰면 웹에서 쓸수있는 wasm이 pkgs폴더에 빌드될거다.
wasm-pack build --target web
html 코드 작성
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta notsus="i use nixos btw">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- <input type="button" value="START" id="puse"><br/> -->
<main id="game">a</main>
</body>
</html>
<script type="module">
import init, { LifeOfGame } from './pkg/wasm_pack_pra.js'
await init() // 초기화
alert("move: arrow key\npuse: space");
let game = LifeOfGame.new(); // 아까만든 게임객채 가저오기
draw();
let PUSE = 1;
let SPEED = 100;
function toggle(i, j) {
game.toggle(i, j);
}
function draw() {
game.draw(window.innerWidth / 20, window.innerHeight / 20);
document.querySelectorAll("div.tile").forEach((button) => {
if (button.id.indexOf(",") != -1) {
// 클릭했을때 세포 반전시키기
button.addEventListener('click', () => {
let [i, j] = button.id.split(",").map(Number);
toggle(i, j);
draw();
});
}
})
}
// 카메라 움직이기
window.onkeydown = (e) => {
if (e.key == "ArrowRight") {
game.move_camera(1, 0);
draw();
} if (e.key == "ArrowLeft") {
game.move_camera(-1, 0);
draw();
} if (e.key == "ArrowDown") {
game.move_camera(0, 1);
draw();
}
if (e.key == "ArrowUp") {
game.move_camera(0, -1);
draw();
}
if (e.key == " ") {
PUSE = !PUSE;
}
console.log(e.key)
}
setInterval(() => {
// 멈추지 않았을때 한번씩 실행시키기
if (!PUSE) {
game.step();
draw();
}
}, 100);
</script>
<style>
* {
background-color: #282828;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
body {
overflow: hidden;
}
main {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
div {
display: flex;
}
div.tile {
border: solid #ffffff28 0.5px;
width: 20px !important;
height: 20px;
/* background-color: red; */
width: fit-content;
&[alive] {
background-color: #fff;
}
}
</style>